[This post is an excerpt from Accountability Technologies, my recently published handbook]
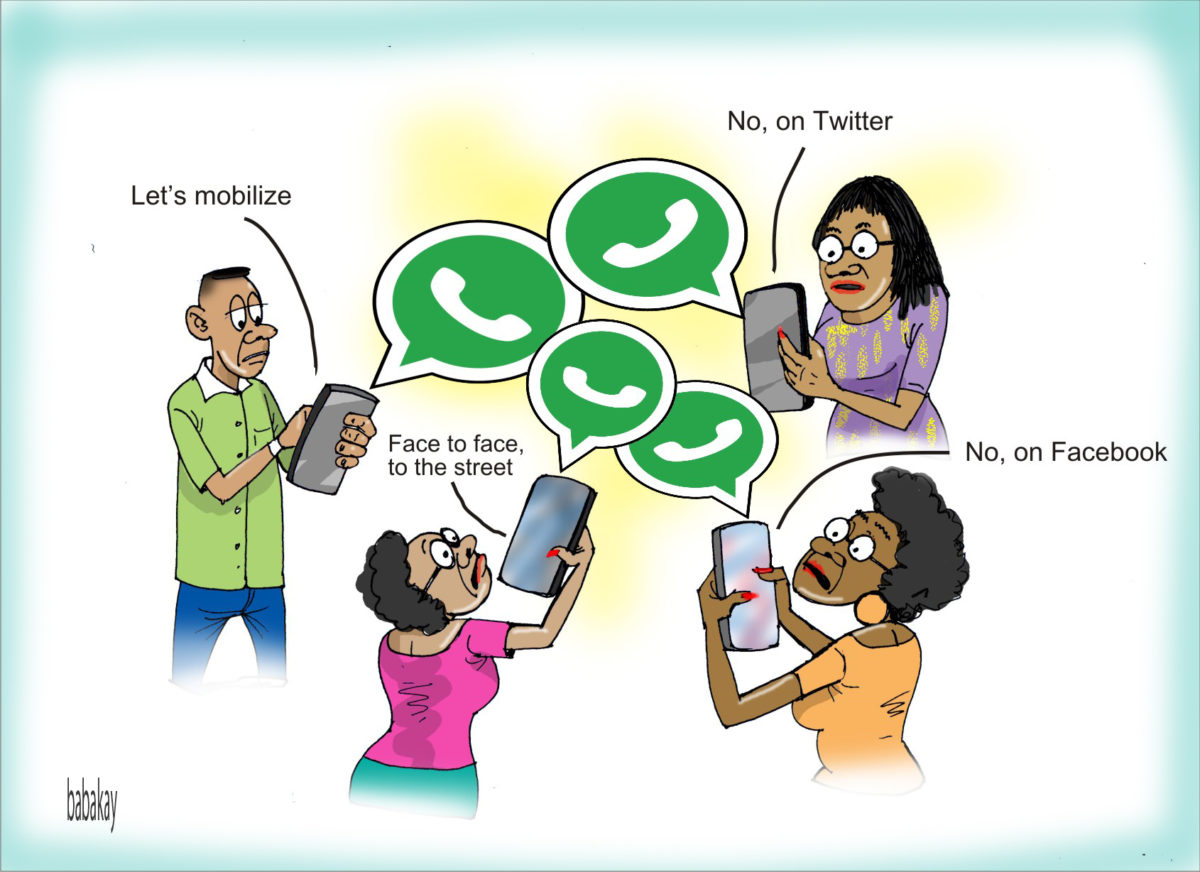
In the second quarter of 2018, popular messaging application WhatsApp achieved 450 million daily active users and it is becoming a favourite technology tool to mobilize citizens and form groups across borders. In 2017, all activists I interviewed in West Africa, for the handbook on Accountability Technologies confirmed that this is becoming a great new tool to mobilize citizens. However, it can be daunting getting citizens and government on the same platform as alluded by Abdul from Network Movement for Democracy and Human Right (NMDH) in Sierra Leone. On NMDH community service delivery project, they added government and Civil Society Organization (CSO) members to a WhatsApp group to exchange information on what concerned government officials can quickly respond to, as it regards service delivery in the health sector. After sometimes, the government officials on the platform had to leave because of false information shared.
Before the 2015 elections in Nigeria, I was able to coordinate 879 election observers in 26 states of the country using WhatsApp as one of the reporting tools for our Ushahidi platform. The WhatsApp group were created for the 26 states, while coordinators were chosen to lead the administration of each group. Police Monitor, an initiative of the Network on Police Reforms in Nigeria (NOPRIN) uses its WhatsApp group to mobilize journalists and activists to hold the police in Nigeria accountable for human rights abuses. The WhatsApp group also had police officials who responded to these abuses. The initiative has since moved to Telegram, as WhatsApp could not contain its over 250+ members. In 2016, when CODE’s Follow The Money was initiating the decentralization of its campaigns, it piloted communications with members using WhatsApp. A group was created by regions for members. After piloting this for 4 months, it became chaotic, as knowledge was lost, and new members couldn’t have access to initiate conversations. The WhatsApp groups have been closed, while the architecture has been transferred to a niche network.
Creating groups on WhatsApp can be frustrating for the administrators, but these simple steps could make it easy to use to meet your objectives. Just in case you have more tips, feel free to put them in the comment box.
- Know the objective of setting up the groups and write down your rules of engagement on the team based on this goal. It is essential to think through what you will achieve with your group, to reduce distractions.
- Create a Code of Conduct. This can be used as a binding agreement between intending members and your organization. CODE’s Follow The Money has a Code of conduct for its 1000+ members.
- Before adding people to the WhatsApp group, inform them about your objective and that you will like to add them to your team. This will allow you to communicate your objective to them, and get feedback from people that will decline.
- Add those that agreed to be on the platform and then post guidelines and rules of engagement.
- As the creator of the group, you must be ready to engage members on issues related to your objective. Set the tone. Some teams fix a time in a week to discuss accountability issues, while another post can be a discussion of the critical problems related to the group objective. Some choose a day for general topics. Most WhatsApp groups are distractions, scheduling conversations could be more fruitful than a free to post at any time, anything – group.
- WhatsApp can be used to spread rumours and fake news swiftly, always verify images, text and videos that are posted using tools like Google Images and TinEye.
- Introduce Perks or Badges, members of your group will be encouraged to discuss better. The Police Monitor Group in Nigeria announces Birthday Greetings for members.
- Whenever you add new participants, send the rules and guidelines immediately.
- Have two or three more administrators that can help in moderating discussions on the platform.
- Democratize the process by requesting a vote for administrators in the coming year. It is a way to show leadership, and show you support participatory democratic systems.
- Encourage members to use emojis on a post sent in by members. It will encourage members to post and facilitates more discussions.